Difference between revisions of "Reflective Shader"
(Updated index of refraction) |
(Updated descriptions of Highlight intensity, Caustic intensity, Reflectivity, Reflectivity tint, & Specular roughness settings, to match those of Glass Shader.) |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| − | *'''Reflectivity: ''' | + | *'''Reflectivity: '''The ability of the surface to reflect light at glancing angles when roughness is low. At glancing angles this proportion is also removed from the transmitted (refracted) light so that it respects laws of energy conservation. In other words, reflectivity controls the blend between reflections and refractions at glancing angles when roughness is low. |
<ul> | <ul> | ||
{| | {| | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
| − | *'''Highlight intensity: ''' This setting | + | *'''Highlight intensity: ''' This setting is a multiplier for the brightness of reflected light from direct light sources only (e.g. Sunlight, Light Source, Spotlight), not indirect reflections. In Terragen 4.4 and above, this also affects the brightness of direct light sources when they're visibly refracted through the surface. For reflections, the only correct value in a physically-based render is 1, but the specular reflection models are not perfect so it's reasonable to change this slightly. |
| + | |||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
{| | {| | ||
| Line 66: | Line 67: | ||
| − | *'''Caustic intensity: ''' | + | *'''Caustic intensity: '''In the real world, light reflecting off or refracting through shiny objects can cause caustics to form on surrounding objects. In the Reflective Shader, the term "caustics" is a bit more specific. It means only those caustics that are reflection/refractions of direct light sources (e.g. the sun), and only those that land on diffuse surfaces or interact with rough reflections/refractions. "Caustic intensity" controls the brightness of the caustics that this Reflective Shader projects onto other objects. Caustics are difficult to sample, so they create unwanted noise in path traced renders and flickering in anything that caches lighting. Terragen tries to improve this by only roughly approximating caustics so they are easier to sample. Despite this they can still be difficult to render well, so "Caustic intensity" lets you control their intensity or turn them off entirely. |
| − | *'''Specular roughness: ''' | + | *'''Specular roughness: ''' The microscopic (or subpixel) roughness of the surface. This roughness causes reflections and refractions to look blurry or diffuse, and it changes the apparent size of highlights from bright sources (due to over-exposure). When rendering with the Standard Renderer the roughness only affects reflections/refractions of direct light sources such as the sun. When rendering with the Path Tracer the roughness is applied more correctly, affecting the blurriness of all kinds of reflections and refractions from the surface. |
<ul> | <ul> | ||
{| | {| | ||
Revision as of 20:15, 26 February 2021
Contents
Overview[edit]
The Reflective Shader provides a reflectivity effect for surfaces which can simulate wet, smooth, and otherwise shiny surfaces. Control is provided over the strength of the reflectivity, the reflection tint, transparency, index of refraction, and whether reflections are Ray Traced.
Settings:
- Enable: When checked, the node is active and the settings below will affect the surface. When unchecked, the node is ignored.
Main Tab[edit]
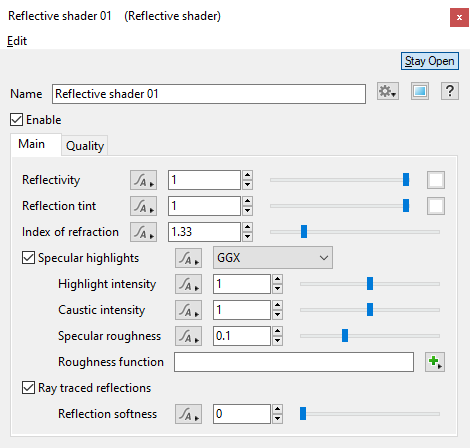
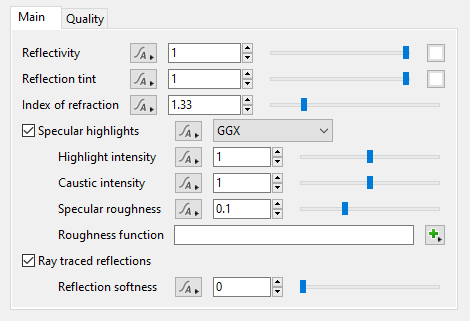
- Reflectivity: The ability of the surface to reflect light at glancing angles when roughness is low. At glancing angles this proportion is also removed from the transmitted (refracted) light so that it respects laws of energy conservation. In other words, reflectivity controls the blend between reflections and refractions at glancing angles when roughness is low.
- Reflection tint: This setting allows you to tint the reflected colours by the color chosen via the Colour picker to the right of the slider.
- Index of refraction: Index of refraction (IOR) is a property of real world materials which affects light refracted into it from another medium. Despite its name it also affects the amount of light reflected off the surface for a given angle; in other words it changes the reflectivity curve which is calculated using the Fresnel equations. In the Reflective Shader the IOR setting must be >= 1. When IOR is exactly 1 there is no reflection. When IOR is greater than 1 some amount of reflection occurs, and the higher the IOR the more visible the reflections. For any IOR > 1, the reflectivity approaches 100% at glancing angles where light travels parallel to the surface (although this can be changed with the Reflectivity setting and roughness also makes it appear to be less). At any other angle the amount of reflection is reduced, calculated from the IOR. The IOR of water is usually around 1.33, depending on conditions, and most types of glass are between 1.4 and 1.9. IOR is rarely higher than 4.0 in real materials. However, you might want to go higher than this to simulate metals. A higher index of refraction can be used to produce higher reflectivity at perpendicular angles, but this is essentially just a cheat and is not a physically-based way to render metal.
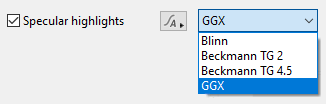
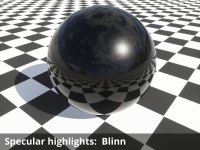
- Specular highlights: This popup has 4 options for choosing the method of calculating the specular highlights.
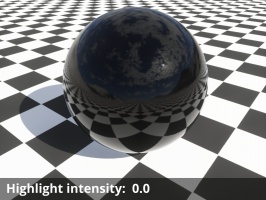
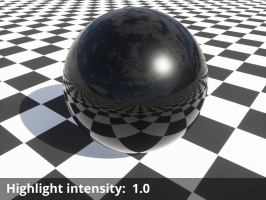
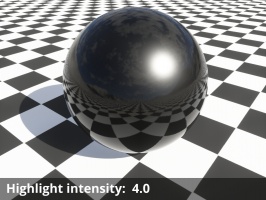
- Highlight intensity: This setting is a multiplier for the brightness of reflected light from direct light sources only (e.g. Sunlight, Light Source, Spotlight), not indirect reflections. In Terragen 4.4 and above, this also affects the brightness of direct light sources when they're visibly refracted through the surface. For reflections, the only correct value in a physically-based render is 1, but the specular reflection models are not perfect so it's reasonable to change this slightly.
- Caustic intensity: In the real world, light reflecting off or refracting through shiny objects can cause caustics to form on surrounding objects. In the Reflective Shader, the term "caustics" is a bit more specific. It means only those caustics that are reflection/refractions of direct light sources (e.g. the sun), and only those that land on diffuse surfaces or interact with rough reflections/refractions. "Caustic intensity" controls the brightness of the caustics that this Reflective Shader projects onto other objects. Caustics are difficult to sample, so they create unwanted noise in path traced renders and flickering in anything that caches lighting. Terragen tries to improve this by only roughly approximating caustics so they are easier to sample. Despite this they can still be difficult to render well, so "Caustic intensity" lets you control their intensity or turn them off entirely.
- Specular roughness: The microscopic (or subpixel) roughness of the surface. This roughness causes reflections and refractions to look blurry or diffuse, and it changes the apparent size of highlights from bright sources (due to over-exposure). When rendering with the Standard Renderer the roughness only affects reflections/refractions of direct light sources such as the sun. When rendering with the Path Tracer the roughness is applied more correctly, affecting the blurriness of all kinds of reflections and refractions from the surface.
- Roughness function: The shader or function nodes assigned to this setting are multiplied by the “Specular roughness” value above which allow you to adjust or break up the intensity of the specular highlight. Note that negative results are clamped to 0.
- Ray traced reflections: When checked, reflections are ray traced for the surface and accurately reflect the scene. When unchecked, only the specular effect will render.
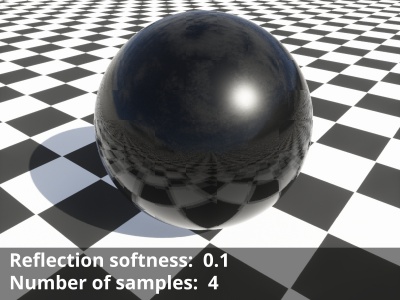
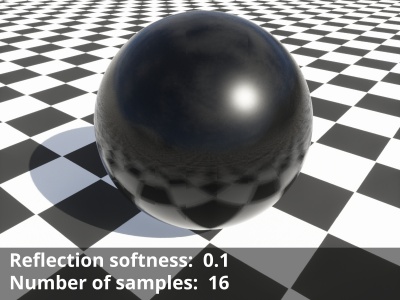
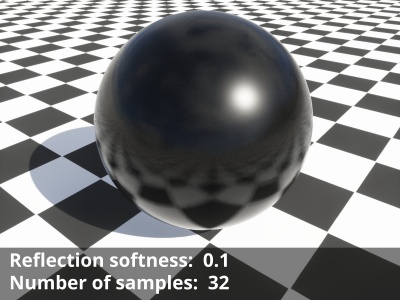
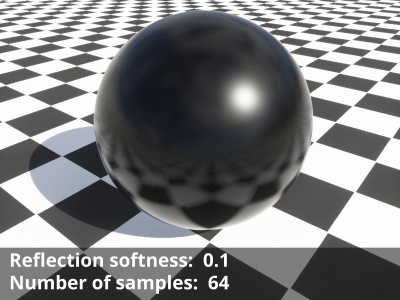
- Reflection softness: Together with the “Number of samples” setting on the Quality tab, this setting controls the blurriness of the reflections. The default value of “0” results in sharp reflections and uses only one sample regardless of the number of samples chosen. Although the slider allows for a large range of values, the recommended range is between 0.0 to 0.1.
Quality Tab[edit]
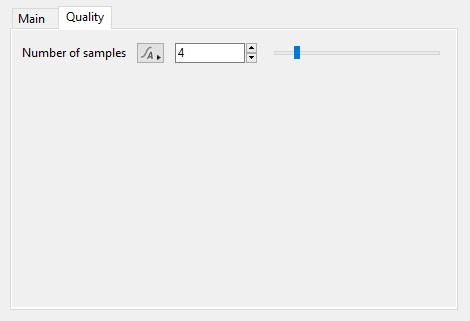
- Number of samples: This setting controls the quality of the soft reflections, which occur when the “Reflection softness” value is greater than “0”. The default value is “4” and raising it will take additional samples leading to a smoother blurred result, at the cost of longer render times.
A sample refers to a value or set of values at a point in time and/or space. The defining point of a sample is that it is a chosen value out of a continuous signal. In Terragen 2 it is usually a mathematical (procedural) function that is being sampled.
A shader is a program or set of instructions used in 3D computer graphics to determine the final surface properties of an object or image. This can include arbitrarily complex descriptions of light absorption and diffusion, texture mapping, reflection and refraction, shadowing, surface displacement and post-processing effects. In Terragen 2 shaders are used to construct and modify almost every element of a scene.