Cos Scalar
Contents
Overview[edit]
These nodes output the cosine, sine or tangent of the Input scalar. If you are using these functions for trigonomic calculations, rather than just for creating a wave shape or similar, you need to be aware that they expect Input values in radians rather than degrees. You can use the Degrees to radians scalar node for the conversion.
These nodes have no other settings apart from the Input node.
Settings:
- Name: This setting allows you to apply a descriptive name to the node, which can be helpful when using multiple Cos Scalar nodes in a project.
- Enable: When checked, the node is active, and when unchecked the node is ignored.
Fun with Cos Scalar[edit]
We can explore the Cos scalar node just as we did for the Sin Scalar node, to see how to create repetitive rows and concentric circles. For step by step instructions click here.
Note how each function outputs a slightly different shape.
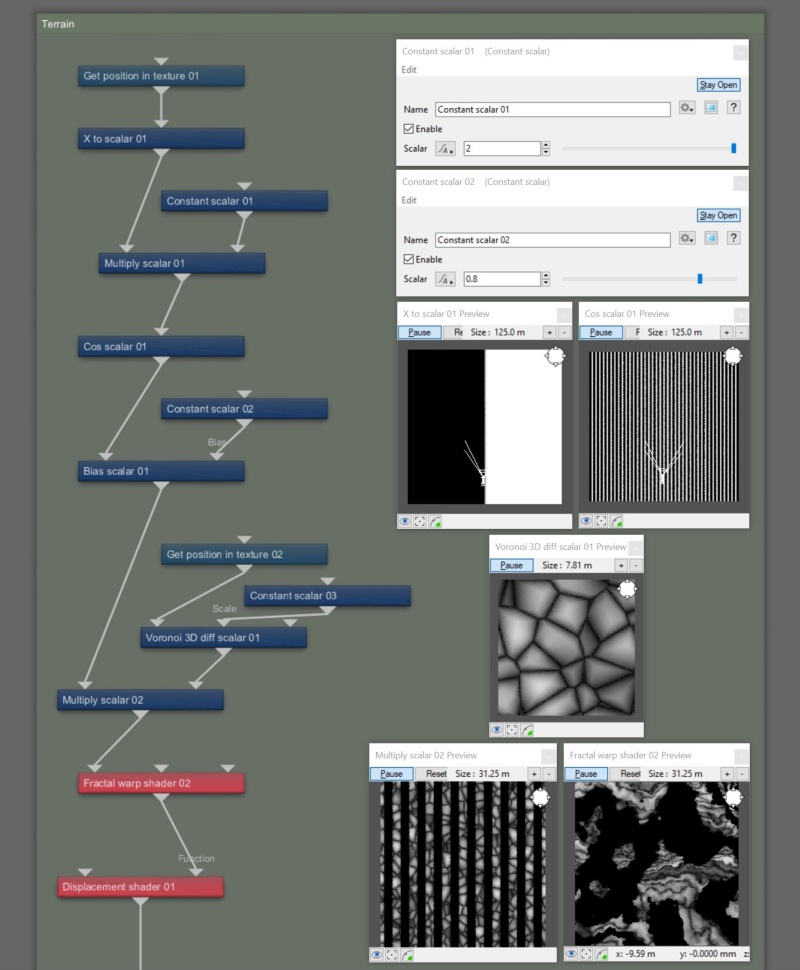
In the image below we see the complete Node Network view for this exploration of the Cos scalar node.
Adjusting the Constant scalar 01 node assigned to the Multiply scalar 01 node allows you to increase or decrease the number of concentric rings or parallel rows.
Adjusting the Constant scalar 02 node, assigned to the Bias scalar 01 node, allows you to modify the profile or curvature of each row or concentric ring.
By multiplying the Bias scalar 01 node by other shader or function nodes you can breakup or mask out parts of the rows and concentric circles. Noise patterns like Perlin and Voronoi are good for this.

|
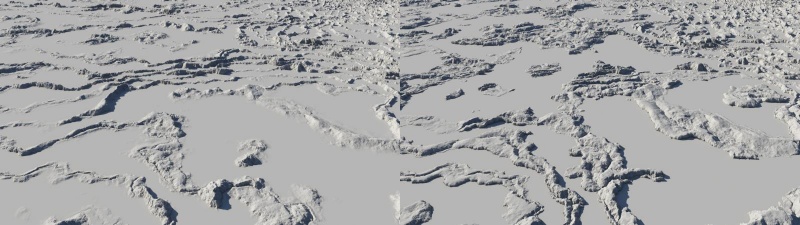
Finally, by applying a warp you can distort the concentric ring pattern or parallel rows to create interesting, organic, and more natural looking forms.
A scalar is a single number. 1, 200.45, -45, -0.2 are all examples of scalar values.
A single object or device in the node network which generates or modifies data and may accept input data or create output data or both, depending on its function. Nodes usually have their own settings which control the data they create or how they modify data passing through them. Nodes are connected together in a network to perform work in a network-based user interface. In Terragen 2 nodes are connected together to describe a scene.
A shader is a program or set of instructions used in 3D computer graphics to determine the final surface properties of an object or image. This can include arbitrarily complex descriptions of light absorption and diffusion, texture mapping, reflection and refraction, shadowing, surface displacement and post-processing effects. In Terragen 2 shaders are used to construct and modify almost every element of a scene.